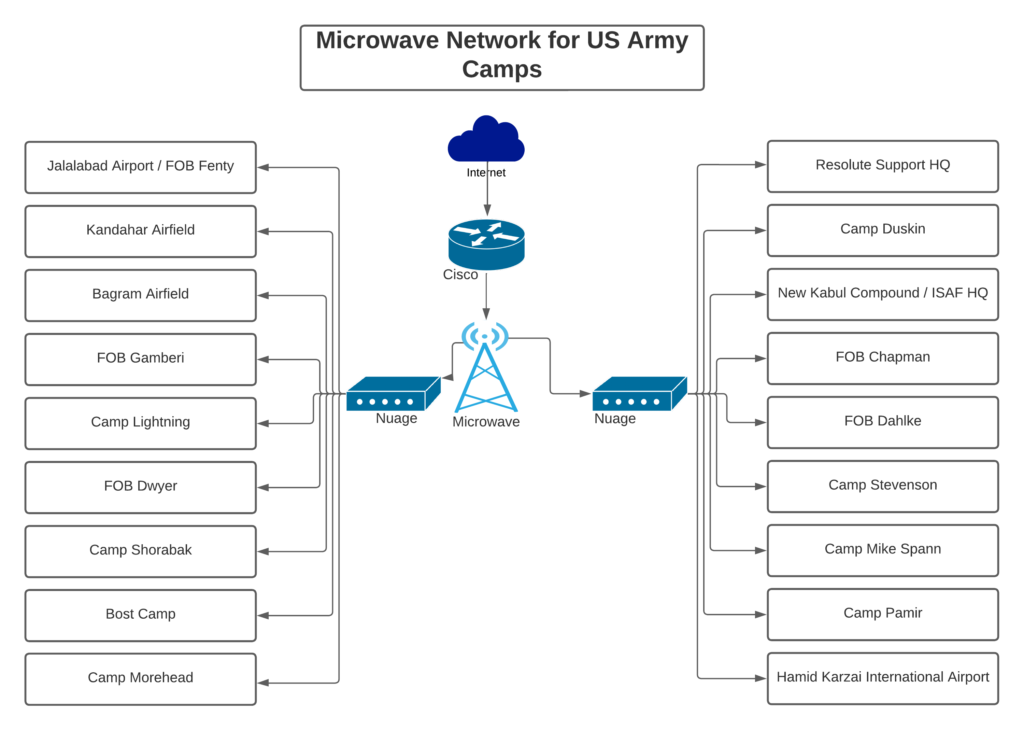
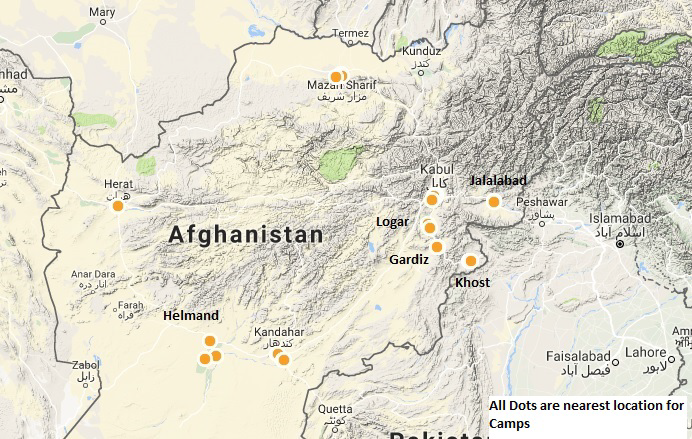
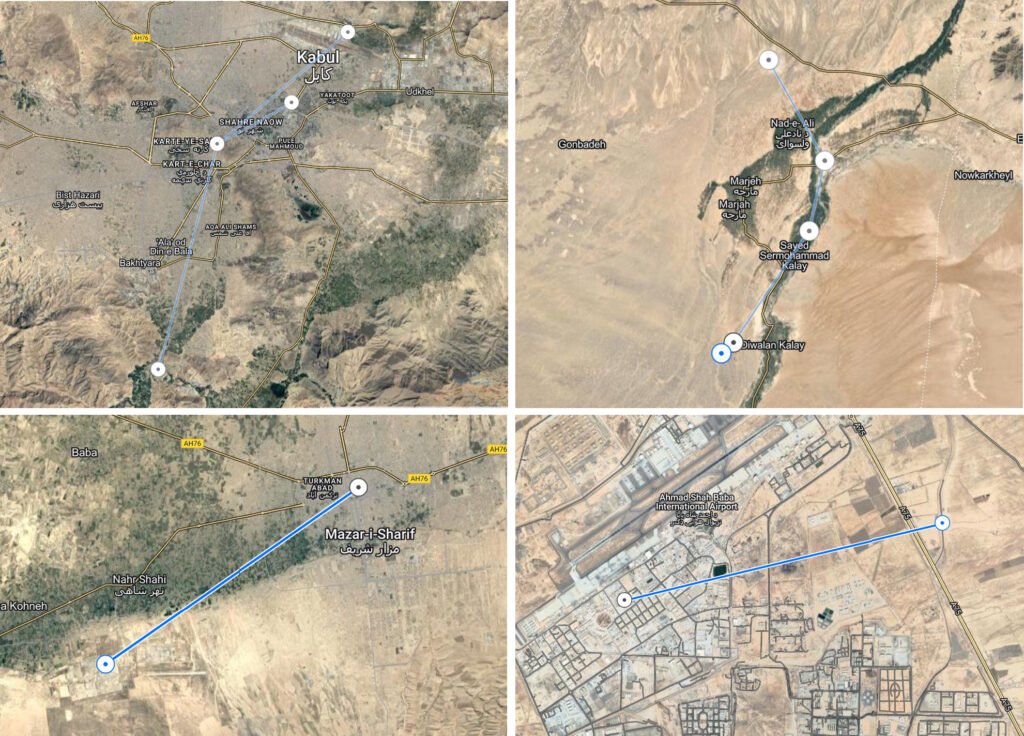
Microwave Solutions
With the development of Information Technology (IT) and the advancement of digital transformation, optical fiber has been widely adopted as a vital means of network transmission. The construction of a large number of information-based sites, such as video security, is bringing numerous challenges to fiber deployment including long construction periods, high costs, difficulties with road and property rights, and issues with deployment on complex terrains. These challenges severely hinder the development of the information industry.
A microwave is an efficient and reliable broadband wireless transmission system, which can effectively solve the problems associated with fiber deployment. About 60% of wireless base stations around the world use microwaves to provide backhaul transmission with large bandwidth and high reliability that covers long distances. In industry, microwaves are mainly used in private emergency communication networks, enterprise private line interconnections, broadband access backhauls, video security, and information site access. microwave equipment provides a maximum of 20 Gbit/s capacity
Microwaves travel by line-of-sight; unlike lower frequency radio waves they do not diffract around hills, follow the earth's surface as ground waves, or reflect from the ionosphere, so terrestrial microwave communication links are limited by the visual horizon to about 40 miles (64 km). At the high end of the band, they are absorbed by gases in the atmosphere, limiting practical communication distances to around a kilometer. Microwaves are widely used in modern technology, for example in point-to-point communication links, wireless networks, microwave radio relay networks, radar, satellite and spacecraft communication, medical diathermy and cancer treatment, remote sensing, radio astronomy, particle accelerators, spectroscopy, industrial heating, collision avoidance systems, garage door openers and keyless entry systems, and for cooking food in microwave ovens.